Theme: Novel Advancements & Therapeutic acuities in Microbial Infection, Immunity & Drug resistance
Antimicrobial Congress 2019
- About the Conference
- Tracks and Sessions
- Market Analysis
- Recent updates on Antimicrobial & Antibacterial agents
ANTIMICROBIAL CONGRESS 2019
Update your skills, enhance your knowledge base, and broaden your horizons- all in one place!
Date: November 11-12, 2019
Venue: Istanbul, Turkey
With great pleasure we welcome all the participants across the World to Attend “2nd International Conference on Antimicrobial & Antibacterial agents” going to be held on November 11-12, 2019 in Istanbul, Turkey.
This conference is held based on the theme “Novel Advancements and Therapeutic Acuities in Microbial Infection, immunity & drug resistance”. This conference provides a firm platform for scientists, researchers, professors, engineers, directors of various companies, industrial professionals and students in the field of microbiology, virology, infectious diseases and other related fields to share their knowledge. We also take immense pleasure in welcoming various professionals from different countries all over the globe.
Antimicrobial Congress 2019 is an international platform for establishing research works and therapeutic findings and disorders based on microbial diseases, viruses and infections caused by bacteria, fungi and protists. These types of diseases may be caused due to water borne, food borne, and air borne in human beings as well as in plants and animals. When it comes to microbiology and virology the microbes are termed as the heart for most of the pressing problems solution in world. It also represents the increasing importance of human mortality around the globe, thereby vaccination and vaccine development plays an important role in terms of global health.
Why to attend?
Our Conference will provide a perfect platform addressing:
• Laudable talks by the top-notch of the global scientific community
• Sterling workshop sessions
• Remarkable Awards and Global Recognition to meritorious Researchers
• Global Networking with 50+ Countries
• Novel Techniques to Benefit Your Research
For more information drop a mail on antimicrobials@globalconferencemeet.com
Targeted Audiences:
- Microbiologists
- Virologists
- Parasitologists
- Bacteriologists
- Pharmacists
- Infectious Diseases Specialists
- Infectious disease researchers, scientists, faculties, students
- Infectious disease association and society
- Pathologists
- Surgeons
- Epidemiologists
- Business entrepreneurs & industrialists
- Deans & HODs
- Directors, Board members, Presidents, vice-president
Conference Opportunities
- Speaker Presentations
- Poster Display
- Symposium hosting (4-5 member team)
- Workshop organizing
- For Researchers and Faculty Members
For Universities, Associations & Societies:
- Association Partnering
- Collaboration proposals
- Academic Partnering
- Group Participation
For Students and Research Scholars
- Poster Competition (Winner will get Best Poster Award)
- Young Researcher Forum (YRF Award to the best presenter)
- Student Attendee
- Group Registrations
For Business Delegates
- Speaker Presentations
- Symposium hosting
- Book Launch event
- Networking opportunities
- Audience participation
For Product Manufacturers
- Exhibitor and Vendor Booths
- Sponsorships opportunities
- Product launch
- Workshop organizing
- Scientific Partnering
- Marketing and Networking with clients
Track 01: Antibiotics, Antimicrobials & Chemotherapy
Antibiotics are used against bacterial infections and some protozoan infections. An antibiotic is an antimicrobial substance who is dynamic against microscopic organisms and is the most important type of antibacterial agents for fighting microbes. Various antimicrobial agents act by interacting with cell wall synthesis, plasma membrane integrity ribosomal function, folate synthesis, and nucleic acid synthesis. The interaction between alcohol and certain antibiotics may occur many cause side-effects and decrease the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. In medicinal chemistry, most modern antimicrobials are a semi-synthetic modification of various natural compounds. The cephalosporin ceftaroline and the lipoglycopeptide oritavancin and telavancin for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection and community-acquired bacterial pneumonia.
Track 02: Vaccines & Vaccinology
Vaccines is a biological preparation that improves immunity to particular diseases. A monovalent vaccine is designed to immunize against a single antigen or single microorganisms. A multivalent or polyvalent immunization is designed to vaccinate against two or more strains of the same microorganisms or two or more microbes. The use of plasmids has been validated in preclinical studies as a preclinical study as defensive immunization procedure for cancer and infectious diseases. Once the altered pathogen is introduced into the bloodstream, it is captured by antigen-presenting cell, which floats around and looking for invaders. A vaccine can prevent outbreaks of contagious diseases through herd immunity.
Track 03: Microbial physiology,Adaptation & Metabolism
Microbial physiology is a scientific concern of life supporting functions and process of bacteria, which allow bacterial cells to grow and reproduce. It is important in the field of metabolic engineering and functional genomics. Microbial adaptation is the ability of microbes to endure the selective pressure of their environment. Bacteria adapt to other environmental conditions as well. These include adaptation to change in temperature, pH, the concentration of ions such as sodium, and the nature of surrounding support. Microbial metabolism is required to live and reproduction of microbes which is obtained from the energy and nutrients.
Track 04: Clinical Microbiology and Medical Microbiology
Clinical microbiology is a incorporate testing for a diverse group of microorganisms. The role of clinical microbiology includes the identification and quantification of microorganisms that cause human disease and to provide diagnostics information for therapeutic support in the clinical management of patients. Medical virologists must also deal with the new threat of bioterrorism, which uses agents like smallpox. Medical microbiology is applied to medicine is a branch of medical science concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of infectious diseases. Therapeutic microbiologists also play a key role in controlling the spread of infectious diseases.
Track 05: Infection & Immunity
Infection is the invasion of an organism’s body tissue by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agents and the toxins by the produce. Infections are caused by infectious agents including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, nematodes such as parasitic roundworms and pinworms, arthropods and microparasites. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Diseases can arise if the host’s protective immune mechanism is compromised and the organisms inflict damage on the host. The immune system response to micro-organism often causes symptoms such as a high fever and inflammation and has the potential to be more devastating than direct damage caused by a microbe.
Track 06: Plant Pathology
Plant pathology is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens and environmental conditions. Organisms that cause infectious diseases include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes, and parasitic plants. Most bacteria that are associated with plants are actually saprotrophic and do harm to the plant itself. A plant becomes diseased when it is continuously disturbed by some casual agent that results in an abnormal physiological process that disrupts the plant normal structure, growth, function or other activities. Control of plant disease is crucial to the reliable production of food and it provides significant reductions in the agricultural use of land, water, fuel, and other inputs.
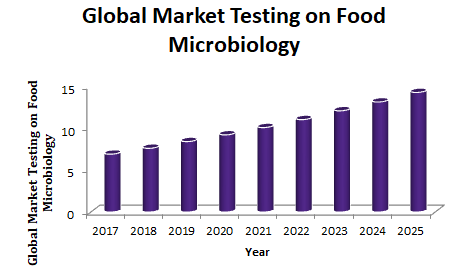
Track 07: Food Microbiology
Food microbiology is the study of the micro-organisms that inhibit, create or contaminate food, including the study of microorganisms causing food spoilage. Fermentation is one of the methods to preserve food and alter its quality. Especially, yeast is used to leaven bread, brew beer and make wine. From the meat and poultry regulatory perspective, we will be addressing bacteria as the main source of food contamination. Bacteria are the most important microbes to the food processor. Human illness caused by foodborne microorganisms are mainly referred to as food poisoning.
Track 08: Industrial Microbiology
Industrial microbiology deals with the production of industrial products in mass quantity. The medical application to industrial microbiology is the production of new drugs synthesized in a specific organism for medical purpose. The commercial production of penicillin and other antibiotics, enzymes, amino acids, alcohols are the most dramatic products in industrial microbiology. Production of antibiotics is necessary for the treatment of many bacterial infections. Microbial inoculants are the addition of microbes into a plant that would essentially help the plant grows by introducing nutrients and stimulating plant growth. Fermentation is a reaction where sugar can be converted into a gas, alcohols or acids. Microorganisms like yeast and bacteria are used to massively produce the many things. Biopesticide is a pesticide derivatized from a living organism or natural occurring substances. Biochemical pesticides can also be produced from naturally occurring substances that can control pest populations in a non-toxic matter. Synthesis of amino acids and organic solvents can also be made using microbes. The synthesis of essential amino acids such as are L-Methionine, L-Lysine, L-Tryptophan and the non-essential amino acid L-Glutamic acid are used today mainly for feed, food, and pharmaceutical industries.
Track 09: Geo Microbiology
Geomicrobiology is the study of microorganisms and earth materials including soil, minerals, rocks, sediment. It concerns the effect of microbes on geological and geochemical processes and vice versa. Some bacteria use material ions as their energy source. Microbes are used to degrade organic and even nuclear waste pollution and assist in the environmental clean-up. Microbial remediation is used in soils to remove contaminants and pollutants. Microbial remediation is used in soils to remove contaminants and pollutants. Microbes play a key role in many biogeochemistry cycles and can affect a variety of soil properties, such as biotransformation of mineral and metal speciation, toxicity, mobility, mineral precipitation, and mineral dissolution. Microbes play a role in the immobilization and detoxification of a variety of elements, such as metals, radionuclides, sulphur & phosphorus.
Track 10: Microbial virulence
The ability of bacteria to cause diseases is described in terms of the number of infecting bacteria, the route of entry into the body, the effects of host defense mechanisms, and intrinsic characteristics of the bacteria called virulence factors. Virus virulence factors allow it to replicate, modify host defenses, allow it to spread within the host and are toxic to the host. During the process of infection, virulence factors of microorganisms combat with the defense mechanism of the host. If virulence factors overcome the defense mechanism of the host, infection is established otherwise microorganisms are eliminated from the host. Pathogenicity of microorganism is determined by nature and type of its virulence effect.
Track 11: Veterinary Microbiology
Veterinary microbiology is concerned with microbial diseases of domesticated vertebrate animals that supply food, other useful products or companionship. Anatomical pathology is concerned with the diagnosis of diseases based on the gross examination, microscopic and molecular examination of organ tissue or whole bodies. Clinical pathology is concerned with the diagnosis of diseases based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluid such as blood, urine or cavity effusions or tissue aspirates using the tools of chemistry, microbiology, hematology and molecular pathology.
Track 12: Soil Microbiology & Agricultural microbiology
Bacteria is a more dominant group of microorganisms in the soil and equal to one half of the microbial biomass in soil. Fungi are more numerous in surface layers well-aerated and cultivated soils dominant in acid soils. Actinomycetes are intermediate group between bacteria and fungi which are widely disturbed in the oil. Algae are present in most of the soils where moisture and sunlight are available. They play a vital role in the maintenance of soil fertility, especially in tropical soils. Most of the protozoa drive their nutrition by feeding or ingesting soil bacteria belonging to the genera. Species of the bacterial genera are commonly used as the food base for isolation and enumeration of soil protozoans.
Track 13: Pharmaceutical Microbiology
Pharmaceutical microbiology gives knowledge about the significance of the presence of bacteria, yeasts, molds, viruses, and toxins in pharmaceutical raw materials, intermediates, products and pharmaceutical production environment. It is a part of industrial microbiology that is responsible for preparation of medications. All parenteral drugs, and many oral drugs, should pass the rigorous microbiological testing in order to validate certain compounds.
Track 14: Bioremediation, Biodegradation & Biodeterioration
Bioremediation is used to treat contaminated media, including water, soil, and surface material by altering environmental conditions to stimulate the growth of microorganisms and degrade the target pollutant. Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi. Any undesirable change in the properties of materials caused by vital activities of organisms is called biodeterioration. It is a most important mechanism for the total removal of chemicals from the environment. As a result, the ability of a chemical to biodegrade is an indispensable element in the understanding of any risk posed by that chemical on the environment.
Track 15: Biofuels & Petroleum Microbiology
Hydrocarbonoclastic microorganisms are petroleum microbiology which degrades hydrocarbons and include a wide distribution of bacteria, methanogen archaea, and some fungi. Current applied research on petroleum microbiology encompasses oil spill remediation, fermentor- and wetland-based hydrocarbon treatment, oil, and fuel upgrading through desulfurization, and microbial community- based site assessment. Bacteria with selected petroleum-metabolizing enzymes amenable to being linked to electronic interfaces are being engineered and developed as biosensors.
Track 16: Biofilms Formation
A biofilm is a community of bacteria that attach to a surface by excreting a sticky, sugary substance that encompasses the bacteria in a matrix. It is composed of a single species or a conglomerate of species. In many cases, biofilms are only bacteria, but they can also include other living things such as fungi and algae, creating a microbial stew of sorts. It is also considered a hydrogel, which is a complex polymer that contains many times its dry weight in water. The biofilm bacteria can share nutrients and are sheltered from harmful factors in the environment, such as desiccation, antibiotics, and a host body’s immune system. A biofilm usually begins to form when a free-swimming bacterium attaches to a surface.
Track 17: Oral Pathology
Oral pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth, jaws, and related structures such as salivary glands, facial muscles, and perioral skin. The clinical evolution and diagnosis of oral mucosal diseases are in the scope of oral medicine practitioners, both the discipline of dentistry. When a microscope evolution is needed, a biopsy is taken , and microscopically observed by a pathologist. In some part of the world, oral and maxillofacial taken on responsibilities in forensic odontology.
Track 18: Human Virology and Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases befall when organisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi come into our bodies and make us sick. These sicknesses can be passed from person to person. Hepatitis is a medical condition defined by the tenderness of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. Hepatitis A is an intense irresistible infection of the liver instigated by the hepatitis A virus. Hepatitis B is an infectious disease instigated by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both intense and chronic infections. HCV is spread mostly by blood-to-blood contact linked with intravenous drug. The IHV focusses in the treatment of HIV/AIDS and other chronic viral diseases, such as Hepatitis C, Hepatitis B, and the Human Papilloma Virus Infection.
Track 19: Viral Oncology
Virology refers to the detailed study of viruses, their structure, shape, habit and habitat. Viral Oncology or Cancer Virology deals with the study of cancer cells. A virus named oncolytic virus tends to infect and destroy the cancer cells. These types of viruses tend to destroy the cancer cells or tumor cells through oncolysis process where they release a new virus cells or virions which help in the destruction of the remaining tumor cells and there by stimulate anti-tumor immune response. Cancer or Tumor virus infections are caused by Oncogenic DNA or RNA viruses.
Track 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
Antibiotics are medications used to kill or slow the growth of bacteria and some fungi. Antibiotics are not effective in treating infections caused by viruses. The definition of antibiotic resistance is the adaptive change in bacteria (mutation) that allows them to grow in the presence of a drug (an antibiotic) that would normally slow their growth or kill them. These antibiotic resistant bacteria and fungi become harder to treat, causing increased morbidity. CDC (Centres for Disease Control and Prevention) statistics show there are approximately 2 million antibiotic resistant infections each year in the United States. According to the WHO (World Health Organization), antibiotic resistant infections can lead to longer hospital stays, higher treatment costs, and more deaths.
Microbiology and virology including other infectious diseases have become increasingly imperative to human society.it has aroused as one of the most important branches of life science. The disease-causing microbes virtually affect all the active region of our body and thus create a great impact towards one’s life. The field of microbiology has made successive progressions in all fields in less time to improve the quality of life. Infectious diseases have almost been dominated by new drugs, genetic engineering technique and the production of new varieties of wines and liquors through microbiology. There is a wide range of scope in the field of microbiology due to its advancements in life science. The scope in this field is immense due to the involvement of microbiology in many fields like medicine, pharmacy, dairy, industry, clinical research, water industry, agriculture, chemical technology, and nanotechnology. There is an increase in a mandate for clinical microbiologists universally. A microbiologist can innovate new diagnostic kits, discover new drugs, teach, research, etc.
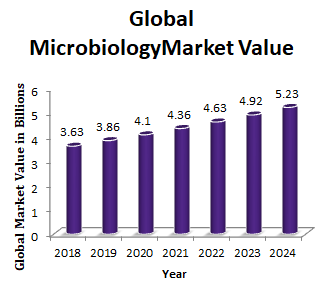
Global Microbiology Testing Analysis Market Report :
The global clinical microbiology market was valued at $3.63 billion in the year 2018 and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% to reach $5.23 billion in 2024. Microbiology testing market is classified into instruments and reagents. In 2018, the instruments product segment accounted for the largest share of the market, however, the reagents product segment is expected to grow at a higher rate during the forecast period. The microbiology testing market is segmented into hospitals and diagnostic centers, custom lab service providers, and academic and research institutes. The key factors driving the growth of this market include ongoing technological advancements in the field of infectious diseases diagnosis, rising incidence of infectious diseases and growth outbreak of epidemics and increased funding and public-private investments for research and innovation.
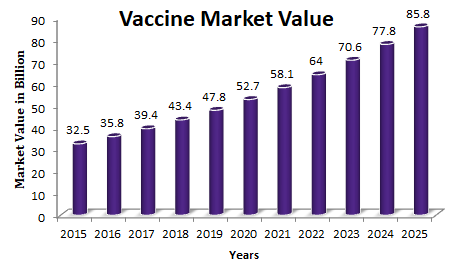
Vaccine Market Report:
Compare to the pharmaceutical market, the vaccine market id relatively small and concentrated on both the supply and demand sides. It is highly regulated and largely dependant on the public purchase and donor policies. The vaccine market has very distinct features, which increase the complexity of assessing and understanding pricing and procurement. It is made up of individual markets for individual vaccines or vaccine type, each with their own specificities, particularly on the supply side. The global vaccine market was valued at over $32.5 billion in 2015 and is expected to reach over $77.8 billion by 2024, at a CAGR of 10.3%.
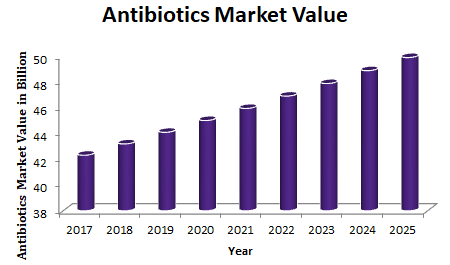
Global Antibiotics Market:
An antibiotic is a chemical compound that kills or slow down the growth of any diseases causing micro-organisms such as bacteria, parasite, and fungi, but is not effective against viruses and prions. Antibiotics act via various mechanisms such as the inhibition of cell wall synthesis, the inhibition nucleic acid synthesis, the disruption of cell membrane, and the inhibition of protein synthesis. The global antibiotics market generated $42.33 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach $49.93 billion by 2025, registering a CAGR of 2.1% from 2018 to 2025. The report covers the present scenario and the growth prospects of global antibiotics market for 2017-2025. The report presents a detailed picture of market by way of study, synthesis and summation of data from multiple sources.
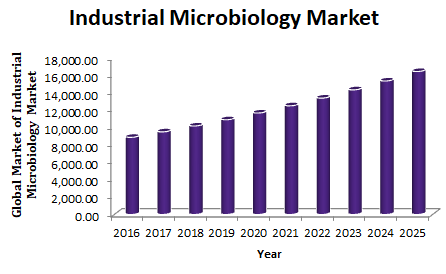
Industrial Microbiology Market:
Industrial microbiology is the application of microbiology technique for management and exploitation of microorganisms for production and processing of useful products on a commercial scale. Industrial microbiology has wide applications in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, agriculture products, industrial chemicals, environment and other. The global industrial microbiology market is estimated to be valued at $ 8,878.2 million by 2016 and projected to grow at CAGR of 7.1% to reach $16,455.0 by 2026 end.
Related Association and Societies:
USA: Federation of American Societies for experimental biology, Federation of American Societies for experimental biology, American society for microbiology, Society for Industrial Microbiology and biotechnology, Society for Applied Microbiology, Society for industrial microbiology, International Union of microbiological societies, Southern California Branch of the American Society for Microbiology, Southeastern Association for clinical microbiology, Association of medical school microbiology and immunology chairs, Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research, The American Association of Immunologists, The American Society for Clinical Investigation, International Union of microbiological societies, Infectious Diseases Society of America, National Foundation for Infectious Diseases
ASIA-PACIFIC: Pan-Pacific Surgical Association Congress, Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies, Malaysian Society of Infectious Diseases, Singapore Society for Microbiology and Biotechnology, Malaysian Society for Microbiology, Asia Pacific Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infection, The Philippine Society for Microbiology, Asia Pacific Society for Marine Biotechnology, Committee of Asia Pacific Electron Microscopy Societies, Federation of Asia Pacific Microbiological Societies, International Union of Microbiological Societies; Microscopy Society (Singapore), Singapore National Academy of Sciences, Japanese Society of Microbial Ecology
EUROPE: Italian Society of Agro-Food and Microbial Biotechnologies, Federation of European Microbiological Societies, European Molecular Biology Organization, Society for Applied Microbiology, Swiss Society for Infectious Disease, European Molecular Biology Organization, International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Federation of European Microbiological Societies, European Society for Clinical Virology, International Union of Microbiological Societies, European Federation of Biotechnology, European Molecular Biology Organization, International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Interregional Association for Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Microorganisms can be the solution of worlds energy problems :
Microorganisms once had an empire on the Earth, thriving by filling every nook and cranny of the environment billions of years before humans first arrived on the scene. The ability of microorganisms to grow from any infinite variety of food sources, rocks, soil, inside roots, compost piles & toxic waste etc. may play a significant role in bailing out our society from the current energy crisis. The Bio design researchers have outlined the paths, where bacteria are the best hope in producing renewable energy in large quantities without damaging the environment or competing with our food supply.
Novel Nano vaccine to treat cancer :
Researchers have developed a novel Nano-vaccine for melanoma, the most aggressive type of skin cancer that begins in melanocytes. Their experiments have proven effective in preventing the development of melanoma and in treating primary tumours and metastases that result from melanoma. The focus of the research was on a nanoparticle that serves as the basis for the new vaccine.
Blocking of new Antibiotic resistant gene :
The researchers identified the gene in a non-toxigenic strain of Vibrio cholerae. Since then, VCC-1 has also been found in non-toxigenic V. cholerae off of the German coastline. The danger is that it's a short jump for a gene from non-toxigenic V. cholerae to its toxigenic siblings.
Conference Highlights
- Antibiotics, Antimicrobial & Chemotherapy
- Vaccines & Vaccinology
- Clinical Microbiology and Medical Microbiology
- Microbial Physiology, Adaptation & Metabolism
- Infection and Immunity
- Plant pathology
- Food Microbiology
- Industrial Microbiology
- Geo Microbiology
- Microbial virulence
- Veterinary Microbiology
- Soil Microbiology & Agricultural Microbiology
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology
- Bioremediation, Biodegradation & Biodeterioration
- Biofuels & Petroleum Microbiology
- Biofilms Formation
- Oral Pathology
- Behavioural Microbiology
- Diagnostic-Microbiology
- Human Virology & Infectious diseases
- Viral Oncology
- Antimicrobial Drug
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 11-12, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by