Theme: Fostering Advances and Applications in the field of Antimicrobial and Antibacterial agents
Antimicrobial Congress 2020
Dear Potential Researchers, Scientists, Industrialists & Students,
Join us for 3rd International Conference on Antimicrobial and Antibacterial Agents
Theme: Fostering Advances, Applications and New Techniques in Antimicrobial and Antibacterial Agents
Update your skills, Meet your academic heroes, Engage in high-level debates and refine your ideas enhance your knowledge base, and broaden your horizons, Visit a new place and have fun, - all in one place!
Date: June 12- 13, 2020
WEBINAR
This conference is based on the theme “Fostering Advances and Applications in the field of Antimicrobial and Antibacterial agents”. This conference provides a firm platform for scientists, researchers, professors, directors of various companies, pharmacists, industrial professionals and young researchers in the field of microbiology, virology, infectious diseases and other related fields to share their knowledge. We also take immense pleasure in welcoming various professionals from different countries all over the globe.
Antimicrobial Congress 2020 is an international platform for establishing research works and therapeutic findings and disorders based on microbial diseases, viruses and infections caused by bacteria, fungi and protists. These types of diseases may be caused due to water borne, food borne, and air borne in human beings as well as in plants and animals. When it comes to microbiology and virology the microbes are termed as the heart for most of the pressing problems solution in world. It also represents the increasing importance of human mortality around the globe, thereby vaccination and vaccine development plays an important role in terms of global health.
For more information drop a mail on antimicrobials@memeetings.com
Targeted Audience :
- Microbiologists
- Virologists
- Parasitologists
- Bacteriologists
- Pharmacists
- Infectious Diseases Specialists
- Infectious disease researchers, scientists, faculties
- Infectious disease association and society
- Pathologists
- Surgeons
- Epidemiologists
- Business entrepreneurs & industrialists
- Deans & HODs
- Directors, Board members, Presidents, vice-president
Conference Opportunities
- Speaker Presentations
- Poster Display
- Symposium hosting (4-5 member team)
- Workshop organizing
- For Researchers and Faculty Members
- For Universities, Associations & Societies:
- Association Partnering
- Collaboration proposals
- Academic Partnering
- Group Participation
- For Students and Research Scholars
- Poster Competition (Winner will get Best Poster Award)
- Young Researcher Forum (YRF Award to the best presenter)
- Student Attendee
- Group Registrations
For Business Delegates
- Speaker Presentations
- Symposium hosting
- Book Launch event
- Networking opportunities
- Audience participation
For Product Manufacturers
- Exhibitor and Vendor Booths
- Sponsorships opportunities
- Product launch
- Workshop organizing
- Scientific Partnering
- Marketing and Networking with clients
1. Antimicrobials
An antimicrobial is an agent that destroys or prevents the development of microorganisms. Antimicrobial medicines may be classified by the micro-organisms against which they primarily function. For example, antibiotics are used to kill and inhibit the growth of bacteria and antifungals are used to kill and inhibit the growth of fungi. They can be categorized according to their function. Agents that inhibit the growth of microbes are called Biostatic agents whereas the agents that kill the microbes are called Microbicidal agents. Classification of Antimicrobials:
Antibacterial
Antifungal
Antiviral
Antiparasitic
2. Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Antimicrobial chemotherapy is the clinical application to treat infectious disease of antimicrobial agents. Different types of drugs such as antibacterial, antifungal, anthelminthic, antiprotozoal, antiviral, etc, are used in antimicrobial chemotherapy. Based on the type of the drug used, Antimicrobial Chemotherapy is classified into following types
Antibacterial chemotherapy
Antifungal chemotherapy
Anthelminthic chemotherapy
Antiprotozoal chemotherapy
Antiviral chemotherapy
3. Clinical/ Medical Microbiology
Clinical Microbiology is a branch of medical science which mainly deals with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of infectious diseases. It is concerned about various clinical applications of microbes for the improvement of health. Clinical Microbiology plays an important role in patient care by providing the cause of infection and antimicrobial susceptibility data to physicians. Rapid diagnosis of pathogens is necessary to facilitate the successful administration of antibiotics and to increase treatment rates. It has different methods of analysis used to identify and isolate the microbes.
Isolation of microbes
Characterization of microbes
Clinical trials
Scope of clinical microbiology
4. Vaccine and Vaccination
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides a specific disease with active acquired immunity. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a microorganism that causes disease and is often produced from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent activates the body's immune system to identify the agent as a threat, kill it, and further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms that may be associated with that agent in the future. Vaccines may be prophylactic (to prevent or reduce possible infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen) or preventive (e.g. cancer vaccines being investigated). Administration of vaccines is called Vaccination. There are various types of vaccines. For example,
Inactivated Vaccine
Attenuated Vaccine
Toxoid Vaccine
Conjugate Vaccine
5. Food Microbiology
Food microbiology is the study of micro-organisms that inhibit, create or contaminate food, including micro-organisms that cause food spoilage, disease-causing pathogens, especially when food is improperly cooked or stored, those used to produce fermented foods such as cheese, yogurt, bread, beer and wine, and those with other useful roles such as probiotics.
Fermented foods
Microorganisms responsible for food spoilage
Microorganisms used in food processing
Probiotics
6. Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Adaptation
Veterinary microbiology deals with domesticated animal microbial (viral, bacterial and fungal) diseases (fellow animals, livestock, fur-bearing animals, fish, game, poultry) that provide food, other useful products or companionship. However, if the pathogens are of concern because of their interrelation with humans (zoonoses) and/or domestic animals, bacterial diseases of wild animals living in captivity or as members of the feral fauna will also be considered. Also included were tests of antimicrobial resistance. Microbial adaptation is the term used to describe microbes ' ability to withstand their environment's selective pressures. For microbial pathogens, such stresses can be due to the biological obstacles of the body and the tissues where they enter to create infection or the immune, antiseptic, or medicinal control measures that we throw at them. While bacteria and parasites can turn on different genes in response to various stimuli, microbial adaptation usually refers to the selection of a genetically distinct microbe population.
Factors affecting microbial diversity
Adaptation of bacteria in aquatic environment
Fungal presence in water environment
7. Microbial Physiology and Metabolism
Microbial physiology is characterized as the study of how, in living organisms, microbial cell structures, growth and metabolism work. It covers the study of viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Microbial metabolism means Microbes obtaining energy and nutrients (e.g. carbon) which are required to live and reproduce. Microbes use many different types of metabolic strategies and organisms dependent on metabolic characteristics can often be distinguished from each other. A microbe's unique metabolic properties are the key factors in determining the ecological niche of that microbe, and often enable that microbe to be useful in industrial processes or to be responsible for biogeochemical cycles. Microbial metabolism is classified based up on three principles:
1. How the organism obtains carbon for synthesizing cell mass:
Autotrophic
Heterotrophic
Mixotrophic
2. How the organism obtains reducing equivalents used either in energy conservation or in biosynthetic reactions:
Lithotrophic
Organotrophic
3. How the organism obtains energy for living and growing:
Chemotrophic
Phototrophic
8. Geo Microbiology
Geomicrobiology is the science field at the geological and microbiological intersection. It concerns the role of microbes in geological and geochemical processes and microbial growth, activity, and survival effects of minerals and metals. Such kind of interactions occurs in the geosphere (rocks, minerals, soils, and sediments), the atmosphere and the hydrosphere. Geomicrobiology studies microorganisms which control the biogeochemical cycles of the Earth, mediate precipitation and dissolution of minerals, and absorb and concentrate metals. The applications include
Bioremediation
Mining
Climate change mitigation
Public drinking water supplies
9. Agricultural Microbiology and Soil Microbiology
Agricultural microbiology is a microbiology branch that discusses plant-associated microbes and diseases of plants and animals. It also addresses soil fertility microbiology, such as microbial degradation of organic matter and transformation of soil nutrients. Soil microbiology is the study of soil microorganisms, their functions and how they affect the properties of soil. It is assumed that the first ancient bacteria and microorganisms came into being on Earth's oceans about two and four billion years ago. Such bacteria could trap nitrogen, compounded over time, and oxygen released into the atmosphere as a result. This resulted in more advanced microorganisms that are significant because they influence the structure and fertility of the soil. Soil microorganisms can be classified as bacteria, actinomycetes, fungi, algae and protozoa. Each of these groups has features that define them and their soil functions.
Bacteria
Actinomycetes
Fungi
Protozoa
10. Pharmaceutical microbiology
Pharmaceutical microbiology is one of the branches of microbiology. This includes, for instance, the study of pharmaceutical microorganisms, reducing the number of microorganisms in a system environment, excluding microorganisms and microbial bi-products such as exotoxin and endotoxin from water and other starting materials, and ensuring that the finished pharmaceutical product is sterile. Certain aspects of pharmaceutical microbiology include research and development of anti-infectious agents, the use of microorganisms to detect mutagenic and carcinogenic behavior in prospective medicines, and the use of microorganisms in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products such as insulin and human growth hormones. Pharmaceutical Microbiology mainly focus on the following:
Drug safety
Antimicrobial activity and disinfectants
Methods and specifications
Cleanrooms and controlled environments
11. Diagnostic microbiology
Diagnostic microbiology is the study of microbial identification. Researchers have been finding ways to extract different species since the invention of disease germ theory. Using methods such as differential media or genome sequencing, physicists and scientists can observe new functions in organisms in order to diagnose organisms more effectively and accurately. Methods used in diagnostic microbiology are often used to take advantage of a particular difference in organisms, often by referring to previous studies, in order to obtain information on which species it may be. New studies provide data that can be cited by other researchers so that scientists can have basic knowledge of the species with which they work.
Automated culturing systems
Blood cultures
Breath tests
Conventional tests
Rapid antigen tests
Biochemical profile- based microbial identification system
12. Microbial Intelligence
The intelligence shown by microorganisms is microbial intelligence (popularly known as bacterial intelligence). The definition includes complex adaptive behavior in single cells and altruistic or cooperative acts in populations of similar or unlike cells mediated by chemical signals that trigger physiological or behavioral changes in cells and influence colony structures. A few examples of Microbial Intelligence are:
Biofilms
Bacterial colony optimization
13. Microorganisms in Recent Drug Discovery
Environmental microbes are a significant source of drug discovery, and several microbial products (anti-tumor products, immunosuppressant, antibiotics and others) are routinely used for human therapy. Most of these products were obtained from cultivable environmental microbes, and this means that the vast majority of microbes were not targeted for drug discovery. With the advent of new and emerging technologies, we are poised to harvest novel drugs from the so-called 'uncultivable' microbes. In this article, we propose how a multidisciplinary approach combining different technologies can expedite and revolutionize drug discovery from uncultivable microbes and examine the current limitations of technologies and strategies to overcome such limitations that might further expand the promise of drugs from environmental microbes.
Novel species discovery
Micos from different areas (patients, geographical locations)
Genetically modified organisms
14. Antibiotic interactions
Antibiotics can interact with a number of other medicines, including prescription, OTC, and natural products. A good practice norm is to obtain a full list of current medications before introducing new antibiotic regimens. If questions arise, a variety of online medication interaction checkers are available, and local pharmacists are happy to serve as a resource. For example:
Drug- Drug interactions
High risk antibiotic drug- drug interactions
Warfarin
Fluor quinolones
Oral Contraceptives
15. Allergic Reactions after Anesthesia & Surgery
An allergic reaction may occur during anesthesia administration but it is not very common. It is estimated that 1 out of every 10,000 patients receiving anesthesia have an allergic reaction during the time following their procedure. This may be attributable to any number of drugs, not just the ones needed for anesthesia. In addition to allergic reactions, nonallergic reactions and side effects of medication can cause symptoms that are easily mistaken for those of an allergic reaction.
During surgery you're exposed to a wide range of materials and medications. Whether the substance irritates your skin, or you are allergic to it, any of these can cause a rash. This is referred to as contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis are usually located in one or two body spots.
Oral medicines given during surgery may also induce rash if you are allergic to any of these. That often called a rash on the drug. Drug rashes are unique in that most body appears to be affected by contact dermatitis.
16. Biofilms Formation
A biofilm comprises any group of syntrophic microorganisms in which cells bind to one another and sometimes also to a surface. Biofilms can form on living or non-living surfaces and can occur in natural, industrial and hospital environments. The microbial cells that grow in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from the same organism's planktonic cells, which, on the other hand, are single cells that can swim or float in a liquid medium. Biofilms can grow on the teeth of most animals as a dental plaque, where they can cause decay and gum disease. In response to various factors, microbes form a biofilm, including cell recognition of specific or non-specific attachment sites on a substrate, nutritional signs, or, in some cases, exposure of planktonic cells to sub-inhibitory antibiotic levels. A cell that switches to the growth mode of biofilm is undergoing a phenotypic behavioral shift in which large gene suites are regulated differently.
Origin of Biofilms
Development of biofilms
Dispersal of biofilms
Properties of biofilms
Extracellular matrix
17. Bioremediation, Biodegradation & Bio deterioration
Bioremediation is used to treat contaminated media, including water, soil, and surface material, by altering environmental conditions to boost micro-organism growth and degrade the target pollutant. Biodegradation is the decay by microorganisms including bacteria, fungi of organic matter. Any excessive alteration in material properties caused by organisms ' essential behaviors is called Bio deterioration. It is the most critical method for the total removal from the atmosphere of chemicals. As a result, a chemical's ability to biodegrade is an essential element in recognizing any threat to the environment posed by that chemical.
Bioremediation related technologies
Phytoremediation
Mycoremediation
Bioventing
Bioleacheing
Landfarming
Mechanism of biodegration
Factors affecting biodegradation rate
Biodegradation vs. composting
Mechanism of bio deterioration
Biodeteriogens
Biodeterioration of organic and inorganic materials
18. Oral Pathology
Oral pathology is the specialty of the discipline of dentistry and pathology that deals with the nature, identification and management of oral and maxillofacial diseases (mouth and jaw). It is a science that examines these diseases ' causes, mechanisms and consequences. Oral pathology practice involves disease research and diagnosis using surgical, radiographic, microscopic, biochemical, or other tests.
Types of oral pathologies
Stomatitis
Tooth resorption
Chronic alveolar osteitis
Maxillary canine extension
Discoloured teeth
Malocclusions
19. Microbial Virulence
Microbial Virulence is the ability of a pathogen or microbe to invade a host or destroy it. Virulence refers to the ability of a pathogen to infect a resistant host in the form of gene for gene systems, often in plants. Virulence refers to the degree of damage done by a microbe to its host in most other contexts, especially in animal systems. An organism's pathogenicity-its disease-causing ability-is determined by its virulence factors. Virulent may characterize either the severity of the disease or the infectiveness of a pathogen. The word virulent is derived from the Latin word virulentus, meaning "toxic wound" or "absolute poison."
Virulent bacteria
Methods by which bacteria cause diseases
Virulent viruses
20. Antimicrobial Agents and Novel Vaccines
By reducing the need for antimicrobial use, vaccines can reduce the prevalence of resistance and also reduce its impact by reducing the total number of cases. Vaccines may allow the use of narrower-spectrum antibiotics for experimental therapy by reducing the number of pathogens that may be responsible for a specific clinical syndrome. Such results can be exacerbated by herd immunity, which extends safety in the population for unvaccinated people. Because a great deal of resistance selection is due to the selection of bystander members of the normal flora, vaccination may reduce resistance pressure even in non-vaccinated pathogens. Many vaccines have disproportionate effects within the target species on drug-resistant lineages, an advantage that could be used more intentionally in vaccine layout.
Hib conjugate vaccine
Respiratory vaccine
15. Allergic Reactions after Anesthesia & Surgery
An allergic reaction may occur during anesthesia administration but it is not very common. It is estimated that 1 out of every 10,000 patients receiving anesthesia have an allergic reaction during the time following their procedure. This may be attributable to any number of drugs, not just the ones needed for anesthesia. In addition to allergic reactions, nonallergic reactions and side effects of medication can cause symptoms that are easily mistaken for those of an allergic reaction.
During surgery you're exposed to a wide range of materials and medications. Whether the substance irritates your skin, or you are allergic to it, any of these can cause a rash. This is referred to as contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis are usually located in one or two body spots.
Oral medicines given during surgery may also induce rash if you are allergic to any of these. That often called a rash on the drug. Drug rashes are unique in that most body appears to be affected by contact dermatitis.
Microbiology and virology including other infectious diseases have become increasingly imperative to human society.it has aroused as one of the most important branches of life science. The microbes that cause disease essentially invade all of our body's active area and thus create a great effect on one's life. The field of microbiology has made successive progressions in all fields in less time to improve the quality of life. New drugs, genetic engineering techniques and the production of new varieties of wines and liquors through microbiology have almost dominated infectious diseases.
Global Antibiotics Market:
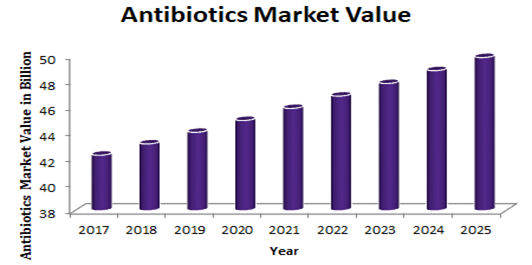
An antibiotic is chemical compounds that kills or slow down the growth of any diseases causing micro-organisms such as bacteria, parasite, and fungi, but is not effective against viruses and prions. Antibiotics act via various mechanisms such as the inhibition of cell wall synthesis, the inhibition nucleic acid synthesis, the disruption of cell membrane, and the inhibition of protein synthesis. The global antibiotics market generated $42.33 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach $49.93 billion by 2025, registering a CAGR of 2.1% from 2018 to 2025. The report covers the present scenario and the growth prospects of global antibiotics market for 2017-2025. The report presents a detailed picture of market by way of study, synthesis and summation of data from multiple sources.
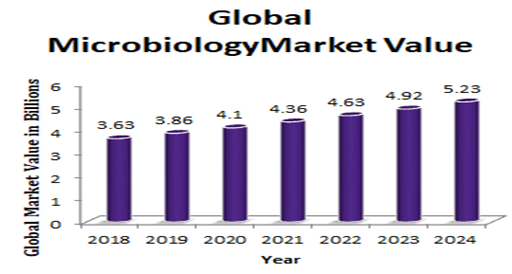
Global Microbiology Testing Analysis Market Report:
The global clinical microbiology market was valued at $3.63 billion in the year 2018 and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% to reach $5.23 billion in 2024. The demand for microbiology research is divided into instruments and reagents. The product segment of instruments accounted for the largest market share in 2018, but the product segment of reagents is expected to grow at a higher rate over the forecast period. The demand for microbiology testing is divided into hospitals and medical centers, specialty laboratory service providers, and educational and research institutes. The key factors driving this market's growth include ongoing technological advances in the treatment of infectious diseases, increased incidence of infectious diseases, and growth outbreaks of epidemics and increased funding and public-private investments for research and innovation.
Industrial microbiology is the application of the technique of microbiology to manage and exploit microorganisms for commercial production and processing of useful products. Industrial microbiology has wide applications in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, agriculture products, industrial chemicals, environment and other. The global industrial microbiology market is estimated to be valued at $ 8,878.2 million by 2016 and projected to grow at CAGR of 7.1% to reach $16,455.0 by 2026 end.
Industrial microbiology is the application of the technique of microbiology to manage and exploit microorganisms for commercial production and processing of useful products. Industrial microbiology has wide applications in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, agriculture products, industrial chemicals, environment and other. The global industrial microbiology market is estimated to be valued at $ 8,878.2 million by 2016 and projected to grow at CAGR of 7.1% to reach $16,455.0 by 2026 end.
Conference Highlights
- Antimicrobials
- Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
- Clinical/ Medical Microbiology
- Vaccine and Vaccination
- Food Microbiology
- Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Adaptation
- Microbial Physiology and Metabolism
- Geo Microbiology
- Agricultural Microbiology and Soil Microbiology
- Pharmaceutical microbiology
- Diagnostic microbiology
- Microbial Intelligence
- Microorganisms in Recent Drug Discovery
- Antibiotic interactions
- Biofilms Formation
- Bioremediation, Biodegradation & Bio deterioration
- Oral Pathology
- Microbial Virulence
- Antimicrobial Agents and Novel Vaccines
- Allergic Reactions after Anesthesia & Surgery
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 12-13, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
- Journal of Food & Industrial Microbiology
- Journal of Medical Microbiology & Diagnosis
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by









